When it comes to welding, two commonly used processes are MIG (Gas Metal Arc Welding) and TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas Welding). Both methods have their strengths and are suitable for different applications. In this article, we will compare MIG and TIG welding, exploring their key differences, advantages, and ideal use cases to help you understand which process may be more appropriate for your welding needs.
Process and Equipment
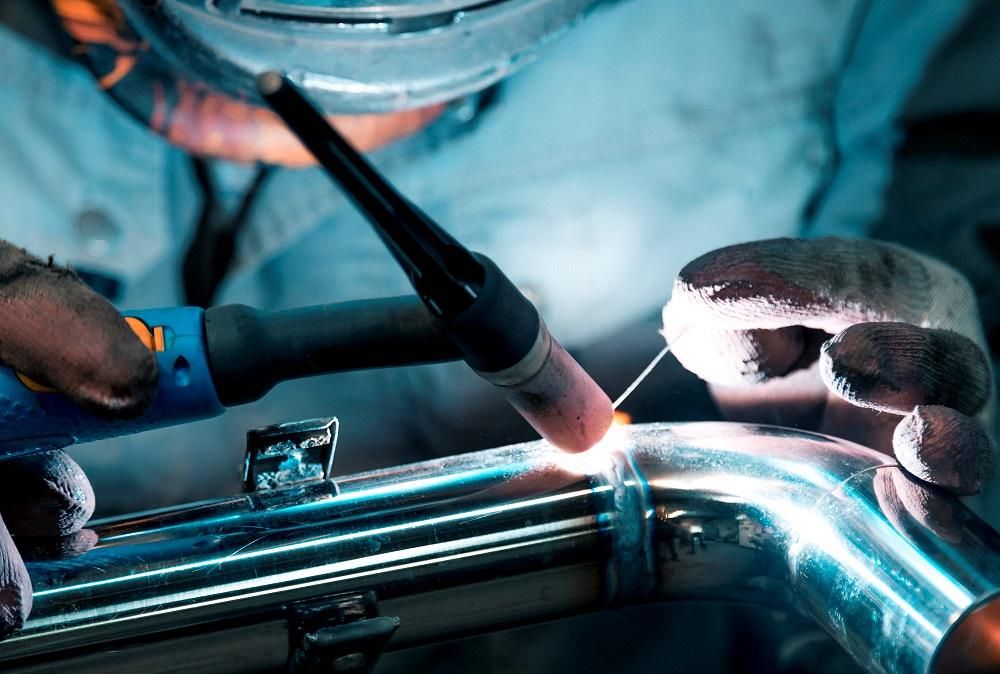
MIG Welding
MIG welding involves feeding a continuous wire electrode through a welding gun, which is connected to a power source. The wire electrode melts and fuses with the base metal, while a shielding gas protects the weld from atmospheric contamination.
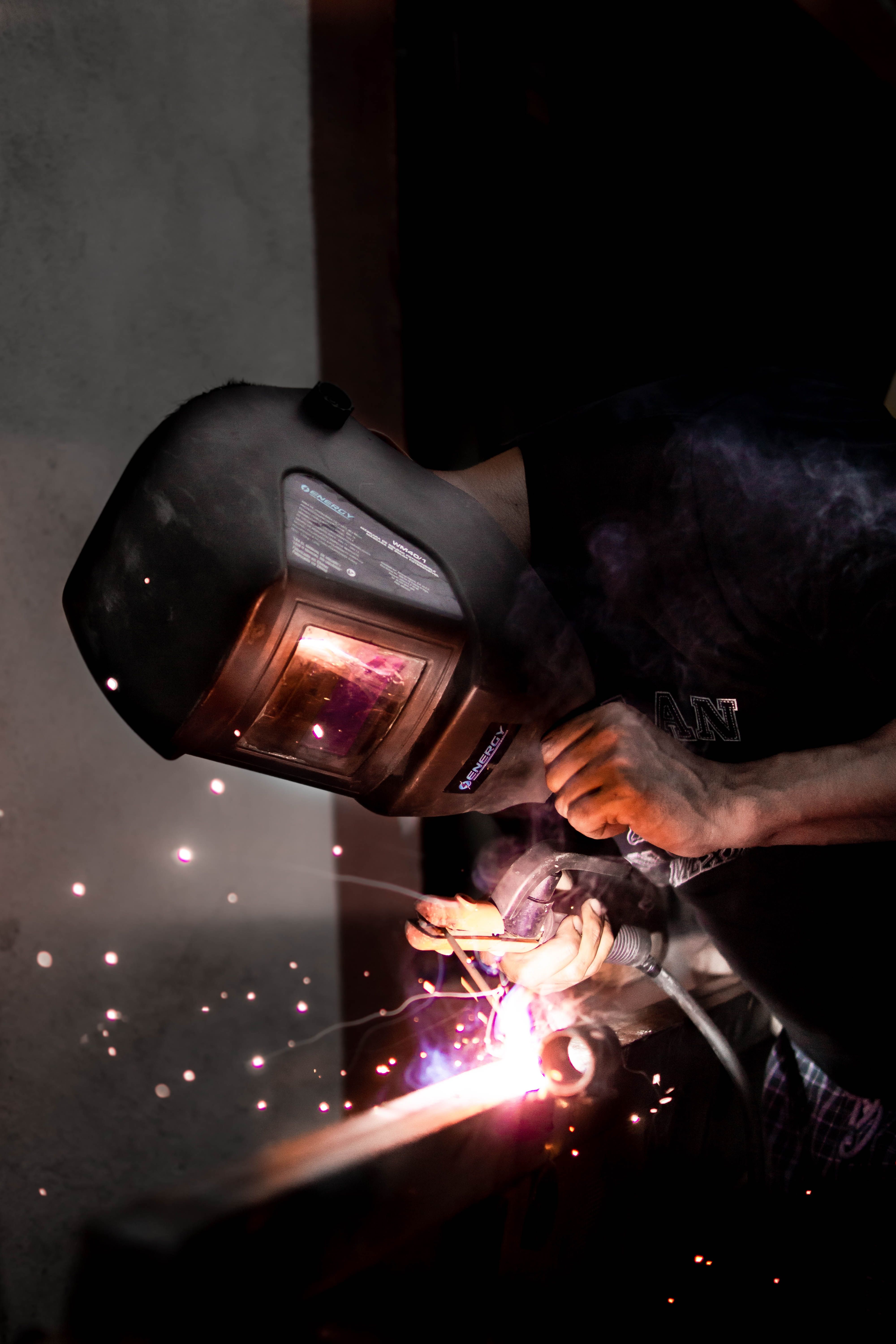
TIG Welding
TIG welding uses a non-consumable tungsten electrode to create an electric arc, which generates the heat required to melt the base metal. A separate filler rod is used if additional material is needed. The weld area is shielded with an inert gas to prevent oxidation.
Application and Material Compatibility
MIG Welding
MIG welding is known for its versatility and is commonly used in automotive, construction, and manufacturing industries. It is suitable for welding thick sections of steel, stainless steel, and aluminum. MIG welding is also preferred for high-volume production due to its speed and efficiency.
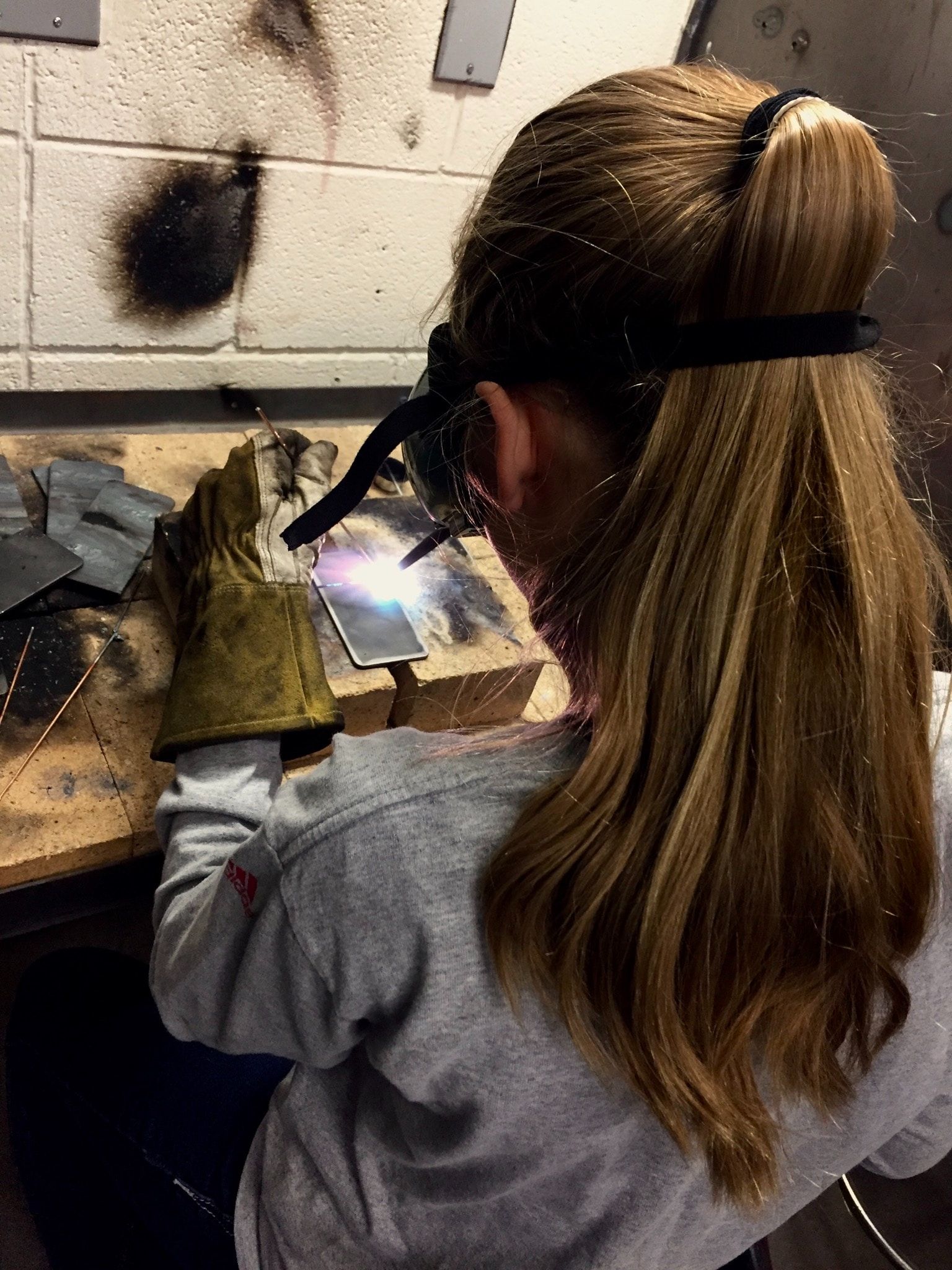
TIG Welding
TIG welding excels in precision and control, making it ideal for critical applications such as aerospace, automotive, and artistic metalwork. It is well-suited for welding thin materials, exotic metals, and non-ferrous metals like aluminum, copper, and titanium.
Skill Level and Weld Quality
MIG Welding
MIG welding is relatively easy to learn and can be mastered quickly, making it suitable for beginners. The process offers good penetration, high deposition rates, and minimal spatter. However, achieving aesthetically pleasing welds may require additional post-weld cleanup.
TIG Welding
TIG welding demands more skill and dexterity, making it better suited for experienced welders. It allows for precise control over the heat input and weld puddle, resulting in high-quality welds with excellent bead appearance and minimal distortion. TIG welding also provides superior weld strength and purity.
Cost Considerations
MIG Welding
MIG welding is generally more cost-effective in terms of equipment and consumables. It requires a lower skill level, and the wire electrode is typically less expensive compared to TIG tungsten electrodes and filler rods.
TIG Welding
TIG welding equipment tends to be more expensive, including the power source, torch, and gas supply. Additionally, tungsten electrodes and filler rods can be costlier. TIG welding also requires more time and skill, which can impact labor costs.
Conclusion
In conclusion, both MIG and TIG welding are valuable processes, each with its own strengths and ideal applications. MIG welding is versatile, efficient, and suitable for a wide range of materials, making it a popular choice for many industries. TIG welding, on the other hand, offers superior precision, control, and weld quality, making it the go-to process for specialized applications and intricate work. Understanding the differences between MIG and TIG welding will help you determine which process aligns best with your welding requirements, skill level, and budget, ensuring successful and satisfactory results in your welding projects.